Cloud Storage vs Local Storage: Key Differences
Cloud Storage vs Local Storage: Key Differences
Choosing between cloud storage and local storage is one of the most important decisions for individuals, startups, and enterprises managing digital data. In Tier-1 countries such as the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, and across Europe, this decision directly impacts cost efficiency, data security, scalability, and long-term business growth.
This detailed guide explains the fundamental differences between cloud storage and local storage, compares their strengths and weaknesses, and helps you decide which option is best based on performance, compliance, security, and cost. The topic is highly relevant to industries such as SaaS, enterprise IT, finance, cybersecurity, and cloud services—industries that attract premium advertisers with very high CPC and eCPM.
What Is Cloud Storage?
Cloud storage is a technology that allows users to store data on remote servers managed by third-party providers and access it over the internet. These servers are hosted in secure data centers and maintained by companies specializing in cloud infrastructure.
Cloud storage eliminates the need for physical hardware ownership, offering on-demand scalability and global accessibility. It is widely used for backups, application data, collaboration, and enterprise workloads.
What Is Local Storage?
Local storage refers to storing data on physical devices such as hard drives, SSDs, USB drives, or on-premise servers located within a home or business environment.
This traditional storage model gives users full control over their data and hardware but requires upfront investment, ongoing maintenance, and physical security management.
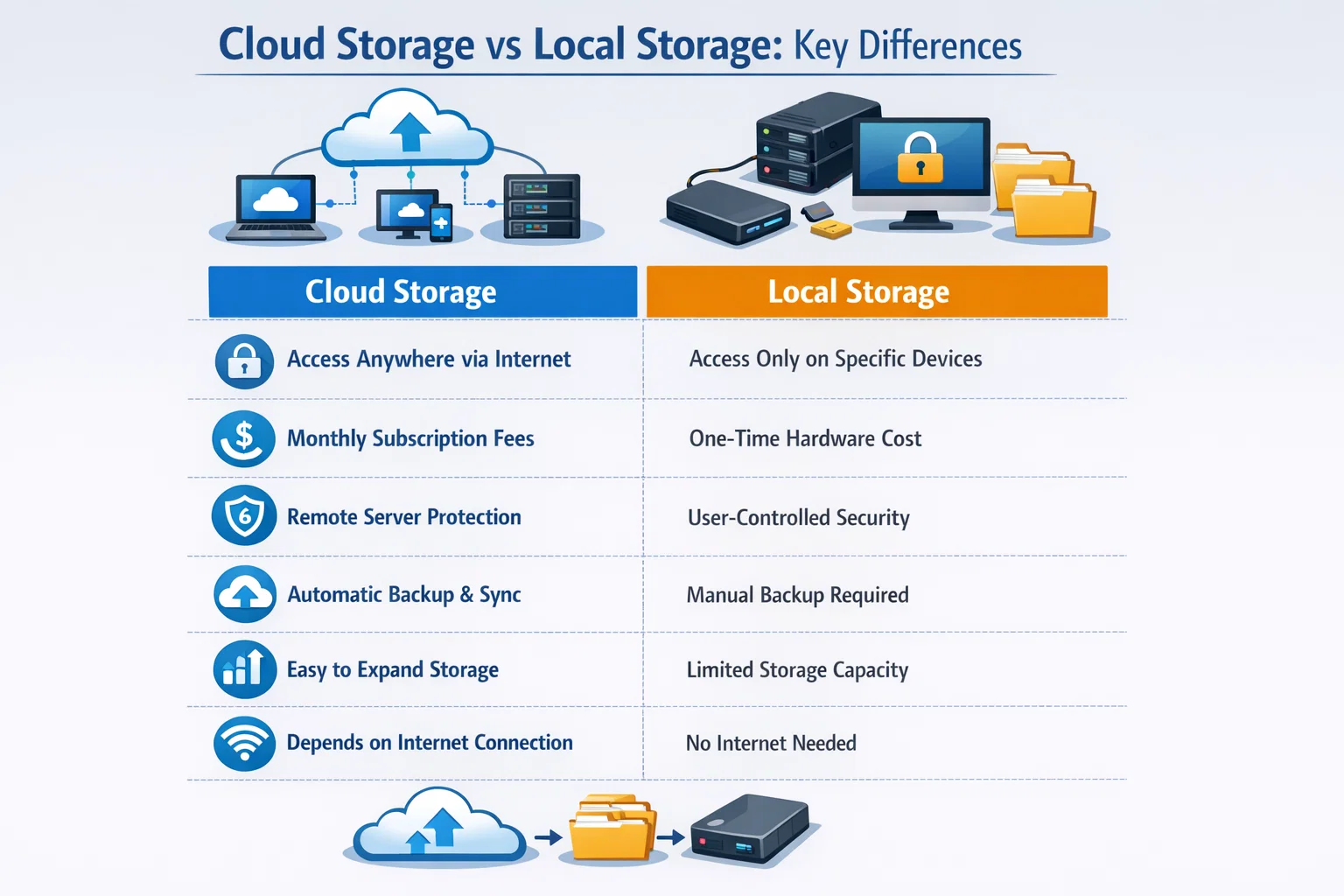
Core Differences Between Cloud Storage and Local Storage
| Feature | Cloud Storage | Local Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Anywhere with internet access | Limited to physical location |
| Scalability | Instant and elastic | Limited by hardware |
| Initial Cost | Low or none | High upfront investment |
| Maintenance | Handled by provider | User-managed |
| Security | Enterprise-grade encryption | Depends on user setup |
Cost Comparison: Cloud Storage vs Local Storage
Cost is often the deciding factor when comparing cloud storage vs local storage. Cloud storage uses a pay-as-you-go pricing model, making it highly attractive for startups and growing businesses.
Local storage requires purchasing hardware, setting up infrastructure, and budgeting for maintenance, upgrades, and potential downtime.
- Cloud storage: Operational expense (OPEX)
- Local storage: Capital expense (CAPEX)
- Cloud storage reduces long-term IT overhead
Security and Data Protection
Security is a critical concern, especially for businesses handling sensitive or regulated data. Cloud storage providers invest heavily in cybersecurity, offering features such as encryption, intrusion detection, and compliance certifications.
Local storage security depends entirely on the user’s ability to implement firewalls, backups, access control, and physical security measures.
Performance and Speed
Local storage typically offers faster read and write speeds because data is accessed directly from physical hardware. This can be beneficial for high-performance workloads like video editing or real-time processing.
Cloud storage performance depends on internet speed and network latency. However, modern cloud providers offer high-speed access through global content delivery networks (CDNs).
Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud storage excels in scalability. Businesses can increase or decrease storage capacity instantly without purchasing new hardware.
Local storage scalability is limited and often requires costly hardware upgrades and downtime.
Backup and Disaster Recovery
Cloud storage includes built-in redundancy and automated backups, making it ideal for disaster recovery and business continuity planning.
Local storage requires manual backup strategies, which are often neglected or improperly implemented, increasing the risk of data loss.
Use Cases for Cloud Storage
- SaaS platforms and web applications
- Remote teams and global collaboration
- Enterprise data backups
- Scalable data analytics
- Compliance-driven industries
Use Cases for Local Storage
- Offline access requirements
- High-speed local processing
- Legacy systems
- Strict on-premise data policies
Hybrid Storage: The Best of Both Worlds
Many enterprises adopt a hybrid approach, combining cloud storage and local storage. This model balances performance, security, and scalability while optimizing costs.
Hybrid storage is especially popular in finance, healthcare, and large enterprises operating across multiple regions.
Cloud Storage and Compliance in Tier-1 Countries
Regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2 influence storage decisions in Tier-1 markets. Leading cloud providers offer compliance-ready solutions that simplify regulatory requirements.
This makes cloud storage highly attractive for high-value industries with strict data protection needs.
Which Is Better: Cloud Storage or Local Storage?
The answer depends on your specific needs. For most modern businesses, cloud storage offers better scalability, security, and cost efficiency. Local storage may still be suitable for specialized performance or offline use cases.
Future Trends in Data Storage
The future of data storage is increasingly cloud-first. Innovations such as AI-driven storage optimization, edge computing, and zero-trust security models are shaping next-generation storage solutions.
Conclusion
Cloud storage vs local storage is not just a technical comparison—it is a strategic decision that affects growth, security, and competitiveness. Understanding their differences helps individuals and businesses make informed choices aligned with long-term goals.
As digital data continues to expand, cloud storage is becoming the preferred choice for scalability, resilience, and global accessibility in today’s digital economy.
Comments (3)